Depth and Skeleton Associated Action Recognition without Online Accessible RGB-D Cameras
Abstract
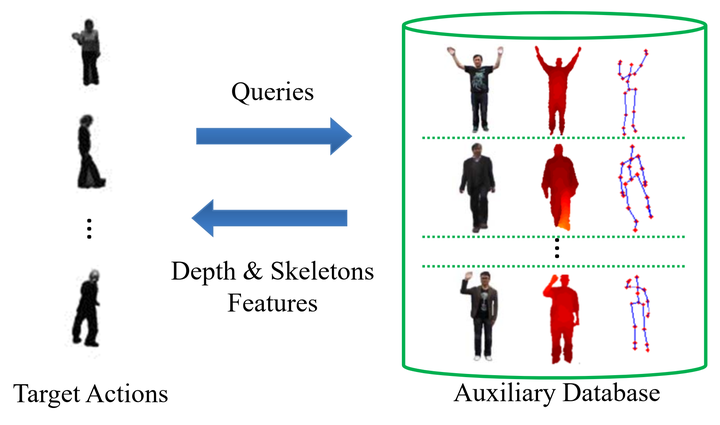
The recent advances in RGB-D cameras have allowed us to better solve increasingly complex computer vision tasks. However, modern RGB-D cameras are still restricted by the short effective distances. The limitation may make RGB-D cameras not online accessible in practice, and degrade their applicability. We propose an alternative scenario to address this problem, and illustrate it with the application to action recognition. We use Kinect to offline collect an auxiliary, multi-modal database, in which not only the RGB videos but also the depth maps and skeleton structures of actions of interest are available. Our approach aims to enhance action recognition in RGB videos by leveraging the extra database. Specifically, it optimizes a feature transformation, by which the actions to be recognized can be concisely reconstructed by entries in the auxiliary database. In this way, the inter-database variations are adapted. More importantly, each action can be augmented with additional depth and skeleton images retrieved from the auxiliary database. The proposed approach has been evaluated on three benchmarks of action recognition. The promising results manifest that the augmented depth and skeleton features can lead to remarkable boost in recognition accuracy.
Resources
Other Links:
Citation
Yen-Yu Lin, Ju-Hsuan Hua, Nick C. Tang, Min-Hung Chen, and Hong-Yuan (Mark) Liao, “Depth and Skeleton Associated Action Recognition without Online Accessible RGB-D Cameras”, IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2014.
BibTex
@inproceedings{lin2014depth,
title={Depth and skeleton associated action recognition without online accessible rgb-d cameras},
author={Lin, Yen-Yu and Hua, Ju-Hsuan and Tang, Nick C and Chen, Min-Hung and Mark Liao, Hong-Yuan},
booktitle={IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
year={2014}
}
Members
Academia Sinica, Taiwan
 |  |  |  |  |
|---|
